China in a decade: New concept spurs greater development, and a new era unleashes stronger dynamic
 0 Comment(s)
0 Comment(s) Print
Print E-mail GMW.cn, October 11, 2022
E-mail GMW.cn, October 11, 2022
IV. Steady pace of coordinated development and continuous optimization of economic structure
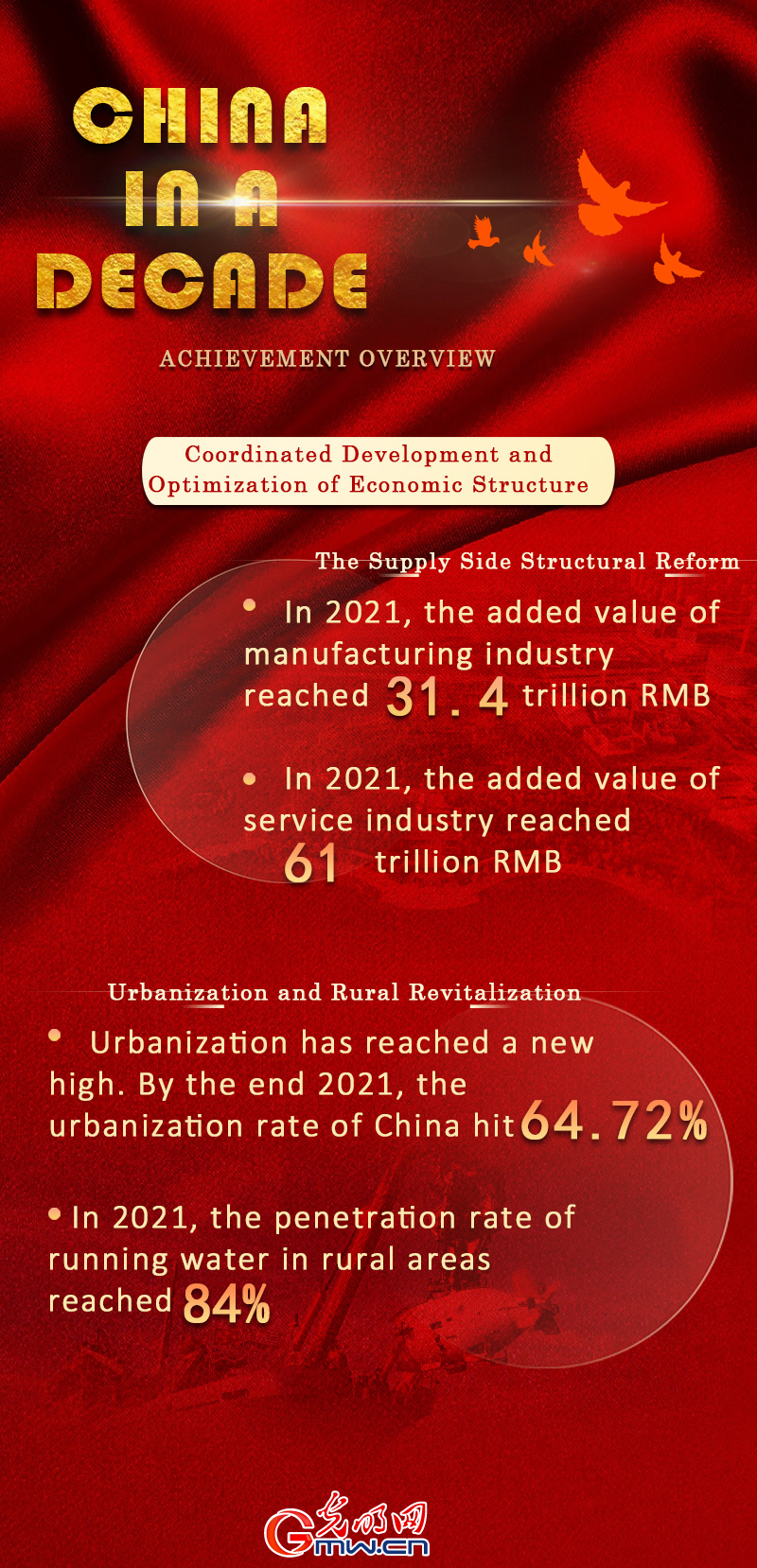
The supply side structural reform has deepened, the strategies of new urbanization and rural revitalization have accelerated their pace of development, economic restructuring is quickened, economic transformation and upgrading have shown effective results, the spatial layout of regional development has been optimized, and China's economy in general has become more balanced, coordinated, and sustainable.
Structural reform on the supply side has been deepened. The “Strong Manufacturing” strategy has pushed China to the medium and premium position of the global industrial chain. In 2021, the added value of manufacturing industry reached 31.4 trillion yuan, an increase of 74.3% over 2012, with an average annual growth rate of 6.4% from 2013 to 2021. In 2013-2021, the added value of high-tech manufacturing and equipment manufacturing enterprises above designated size increased by 11.6% and 9.2% respectively, 4.8 and 2.4 percentage points faster than that of industrial enterprises above designated size. The service industry has grown both in terms of quality and quantity. In 2021, the added value of service industry reached 61.0 trillion yuan, an increase of 90.7% over 2012, with an average annual growth of 7.4% from 2013 to 2021; The service sector accounted for 53.3% of China's GDP, up 7.8 percentage points against 2013. Labor productivity continues to improve. In 2021, total labor productivity (by 2020 prices) hit 146,380 yuan per person, up 80.3% from 2012, with an average annual growth rate of 6.8% from 2013-2021.
New urbanization and rural revitalization have been solidly promoted. Urbanization has reached a new high. As of end 2021, the urbanization rate of China hit 64.72%, up 11.62 percentage points from the end of 2012, with an average annual increase of 1.29 percentage points. In 2021, the penetration rate of running water in rural areas reached 84%, all villages were connected to broadband, and all villages above designated size were connected to hardened roads. The gap between urban and rural development has been further narrowed. The ratio of per capita disposable income of urban and rural residents reduced from 2.88 in 2012 to 2.50 in 2021, and the ratio of per capita consumption was reduced from 2.57 to 1.90.





